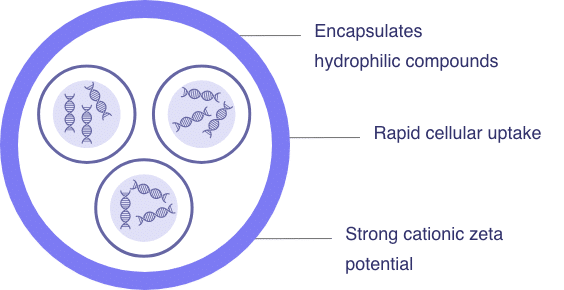
What are Amphipathic Peptide Capsules (APC)?
APC are an entirely new class of nanocarrier engineered from the sequence of a naturally occurring protein. They allow for the efficient encapsulation and improved cellular uptake of nucleic acids and water-soluble compounds. Due to their high positive surface charge, APC can readily penetrate mucosal membranes for delivery of therapeutics. The surface of APC allows for attachment of targeting moieties, ensuring active ingredients are delivered precisely to the cells where they are needed.
APC Advantages

Water soluble
Non-immunogenic

Stable at room temperature
(Releases contents in cells)

Minimally toxic to cells
Easily metabolized
How Does It Work? Here are the steps for APC Payload Delivery:

Step 1
The positively charged surface of APC meets a cell membrane.
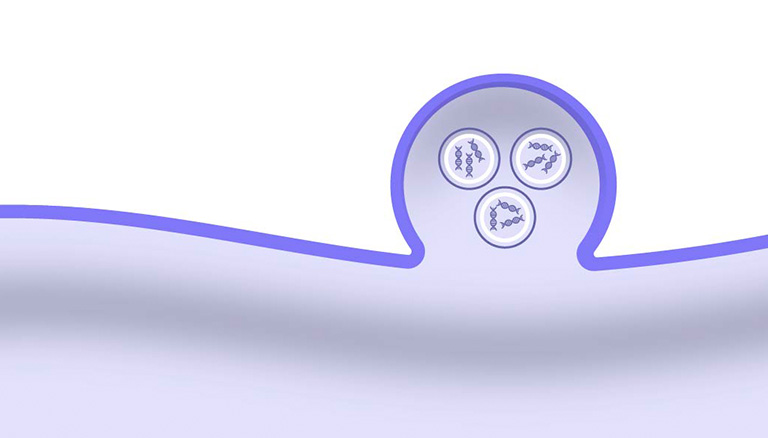
Step 2
The cell membrane envelopes APC and their cargo, forming an early endosome.

Step 3
APC begin to breakdown in the late endosome releasing their contents in the perinuclear cytosol.

Step 4
The new pH results in a reduction of electrostatic attraction, and the surface payload is released.

Step 5
Nucleic acids and any other encapsulated contents are released from the APC into the cytosol.
Applications for In Vitro and In Vivo Research
APC are rapidly taken up by all cells tested to-date. They enter cells through the endocytic pathway and are later metabolized in the cells. APC have been shown to effectively deliver nucleic acids, which are released in a time-dependent manner. They show negligible cytotoxicity when given at doses that exceed clinically relevant doses in cultured cells, fungi and insects. Working with APC makes it simple to move from in vitro research to in vivo applications.